PD2AF Converter
PD2AF converter is an open-source application designed to enable communication between the Process Description and the Activity Flow languages of the SBGN standard. The PD2AF tool is built on and further develops the logic of the previously published template-based translation from PD to AF (Vogt et al., 2013, doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-7-115) which is accessible as a functionality of the SBGN-ED add-on of the VANTED editor.
The purpose of the new tool is to translate PD to AF in such a way so it is possible to avoid using complexes in the resulting AF version and therefore be as close as possible to manually designed AF diagrams and the corresponding logical models. The converter uses the concept of the SBGN Bricks and additionally detects advanced network patterns such as, for example, “hidden” inhibition, when the mechanism is shown in details and no inhibition arcs are used.
The code is written in Lisp.
Availability
Online conversion (daily updates): http://pd2af.me/
Online conversion (stable version): http://pd2af.org/
Github: https://github.com/prozion/pd2af
Contributors
Denis Shirshov, European Institute for Systems Biology and Medicine, Lyon, France
Alexander Mazein, European Institute for Systems Biology and Medicine, Lyon, France
Anatoly Sorokin, Institute of Cell Biophysics, Russian Academy of Science, Pushchino, Russia
Irina Balaur, European Institute for Systems Biology and Medicine, Lyon, France
Johann Pellet, European Institute for Systems Biology and Medicine, Lyon, France
Charles Auffray, European Institute for Systems Biology and Medicine, Lyon, France
PD2AF 1.0
The implemented logic is based on the work by Vogt and coauthors (Vogt et al., 2013, doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-7-115) and further developed to minimise the number of complexes in AF version and to introduce pattern recognition functionalities.
What is new in PD2AF 1.0:
- The code is written from scratch in Lisp programming language and made easily accessible on Github.
- Added pattern recognition for removing “intermediate” complexes.
- Added pattern recognition for some types of inhibition shown in details without using the inhibition arc.
Development plan
The development is planned in a stepwise manner and assumes the following milestones.
PD2AF Milestone #1 Basic - “Enhanced” version - Automatic
PD2AF Milestone #2 Intermediate - “Adviser” version - Semi-automatic
PD2AF Milestone #3 Advanced - “Informed guess” version - Automatic
Translation rules
Protein activation by phosphorylation
 SBGN-ML Newt |
 SBGN-ML Newt |
This translation is conditional. It assumes that 1) the unphosphorylated state is not active, i.e. there are no outgoing regulatory arcs, 2) the resulting state is active towards another process, i.e. there are outgoing regulatory arcs or there could be (might not be shown on the diagram). |
 SBGN-ML Newt |
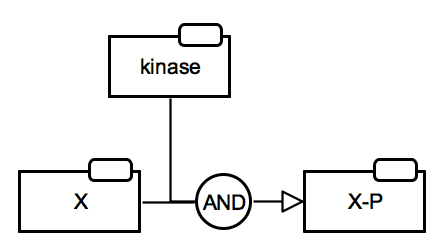 SBGN-ML Newt |
Translation of the case when it is necessary to show two activities of the same protein, i.e. there are outgoing regulatory arcs from both states in PD. An example case is the phosphorylation of bifuntional enzyme PFK by PKA. |
Advanced patterns: “hidden” inhibition
Inhibition pattern 1: inhibition by activation of a competitive process
Condition: the macromolecule B in states B0 and B2 do not have outgoing regulatory links (are not active).

SBGN-ML Newt |

SBGN-ML Newt |
| Variant 1 | |

SBGN-ML Newt |

SBGN-ML Newt |
| Variant 2 | |
Inhibition by complex formation

SBGN-ML Newt |

SBGN-ML Newt |
| Implicit inhibition by complex formation | |
Multiple active states for the same element

SBGN-ML Newt |

SBGN-ML Newt |
| Two active states | |
Examples
Comparison
Unsolved cases
Text